Configure mTLS
Mutual Transport Layer Security (mTLS) is a security protocol that enhances the traditional Transport Layer Security (TLS) by requiring both the server and the client to authenticate each other. In a typical TLS handshake, the server is authenticated to the client, but in mTLS, the client also presents a digital certificate for authentication to the server. This mutual authentication adds an extra layer of security, ensuring that both parties can trust each other's identity. Once the authentication is successful, secure communication is established with the encryption of data exchanged between the client and the server.
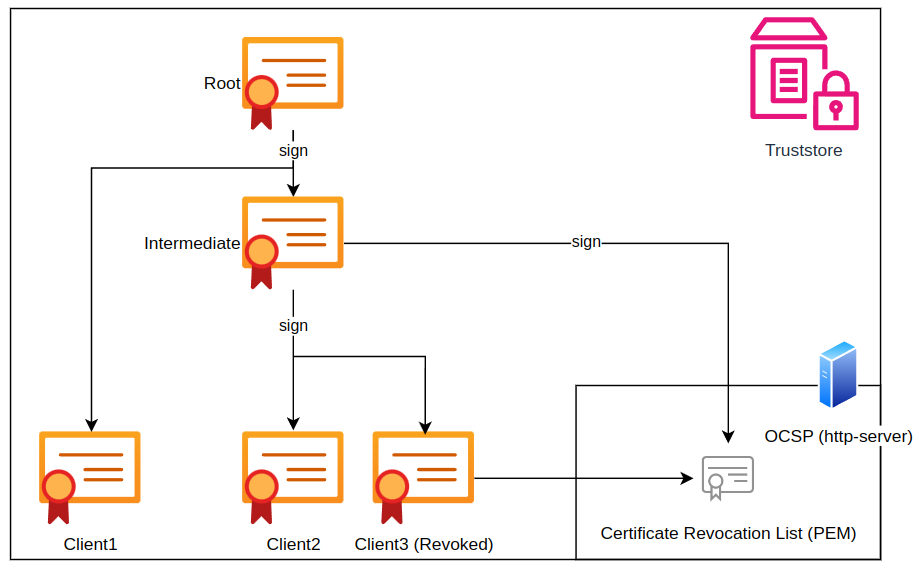
In the following you are going to create the root, intermediate and Client 2 Certificates and keys in order to demonstrate a successful mTLS setup.
CloudsHSM - TSBaaS (dedicated instance)
Initial Setup
As a TSBaaS customer, you must provide the Securosys Support Team with a valid client certificate to establish the initial trust. The following guide shows how to generate a client certificate using OpenSSL.
Note that some organizations may prefer to use their own Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) or certificate utility.
Generating a Client Certificate with OpenSSL:
Root
openssl req -new -x509 -nodes -sha256 -newkey rsa:4096 -days 3650 -subj '/CN=localhost' -keyout ca.key -out ca.crt
Intermediate
openssl genrsa -out intermediate.key 4096
openssl req -new -subj "/CN=intermediate" -key intermediate.key -out intermediate.csr
openssl x509 -req -in intermediate.csr -sha256 -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650 -out intermediate.crt
Client 2 (singed by intermediate cert)
openssl genrsa -out client-singed-by-inermediate.key 4096
openssl req -new -subj "/CN=client-singed-by-inermediate" -key client-singed-by-inermediate.key -out client-singed-by-inermediate.csr
openssl x509 -req -in client-singed-by-inermediate.csr -sha256 -CA intermediate.crt -CAkey intermediate.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650 -out client-singed-by-inermediate.crt
Action: Send either the intermediate or client-certificate to Securosys Support Team. We will setup your service accordingly and notify you.
Revoke Access / Trust a new certificate
To manage (add/remove) trusted client certificates, you have two options:
Please note that any security policy change acquired via a support ticket incurs a service fee. To limit this cost and increase your flexibility, you may use your own OCSP server to manage trust.
- Manual Trust Management
- OCSP
-
Create Support Ticket
- Submit a support ticket with instructions on adding or removing a client certificate.
- Use the following Ticket Type: 5 - Change request -> CloudHSM -> Security Policy Change
Note: Only Security Manager Clouds are authorized to make Security Change requests.
The Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) is used to check the revocation status of digital certificates in real-time. This allows TSB to verify whether a client certificate has been revoked or remains valid. Note that this check is executed on each request and may introduce a delay.
Setting Up an OCSP Responder
You have the following options for deploying an OCSP responder:
- Deploy your own OCSP responder.
- Use an OCSP responder from your PKI.
- Use an OCSP responder provided by AWS.
Configuring the Client Certificate
Ensure your client certificate includes the following X509v3 extension to specify the OCSP responder:
X509v3 extensions:
Authority Information Access:
OCSP - URI:http://<your-ocsp-responder>.com
Replace <your-ocsp-responder>.com with the actual URI of your OCSP responder.
Attention
Since the revocation status check (OCSP) is an external service not controlled by Securosys and is performed on every request, the OCSP service is explicitly excluded from the Service Level Agreement (SLA) between Securosys and its clients. Therefore, please ensure you have optimal availability for your OCSP service.
On-Premise Deployment
Add the Client Certificate (Public) to Server-TrustStore:
keytool -importcert -keystore securosys-ska-truststore-server.jks -alias client-signed-by-intermediate-public -file client-singed-by-inermediate.crt -storepass secret
-
Copy the generated
securosys-ska-truststore-server.jksfile to theconfig-files/tlsfolder within the securosys-tsb directory. Create the**tls**directory if it does not exist. -
Modify the following properties in the application-local.yml file:
# Trust-Store configuration (m)TLS
server:
ssl:
# add client certificates and/or CA's to the trustStore if you want mTLS, otherwise comment out.
trust-store: 'file:/etc/app/config/tls/securosys-ska-truststore-server.jks'
trust-store-password: secret # yourTrustStorePassword
trust-store-type: jks
# (Enum: `need` [Client authentication is needed and mandatory], `none` [Client authentication is not wanted], `want` [Client authentication is wanted but not mandatory])
client-auth: need
- Run or restart the Docker container:
docker-compose down
docker-compose up
Generating PKCS12 Container for Client Truststore
To facilitate usage with both CURL and web browsers, generate a PKCS12 container for Client2.
openssl pkcs12 -export -out client-truststore-CLIENT_SIGNED_BY_INTERMEDIATE.p12 -inkey client-singed-by-inermediate.key -in client-singed-by-inermediate.crt -password pass:secret
This command creates a PKCS12 container named client-truststore-CLIENT_SIGNED_BY_INTERMEDIATE.p12, incorporating the private key (client-signed-by-intermediate.key) and the corresponding certificate (client-signed-by-intermediate.crt). The password for the container is set to secret.
Testing with CURL
Do not use the --insecure flag in productive environment, replace it with the --cacert flag or use a public CA instead.
curl -v --insecure --cert-type P12 --cert client-truststore-CLIENT_SIGNED_BY_INTERMEDIATE.p12:secret https://localhost:8080/v1/key